AI Legal Research: Transforming the Legal Industry
Table of Contents
- Understanding Semantic Search vs. Keyword Search in Legal Research
- Citation Network Analysis: Graph Neural Networks and Legal Importance
- RAG Architecture: Combining Retrieval with Generation
- Lexis+ AI: Architecture and Capabilities
- Westlaw CoCounsel: Model Agnostic RAG Implementation
- vLex Vincent: Multi-Model Global Architecture
- Citation Verification Systems: Shepard’s and KeyCite
- Hallucination Rates and Accuracy Concerns
- Best Practices for Using AI Legal Research Tools
- Conclusion
- Understanding Semantic Search vs. Keyword Search in Legal Research
- Citation Network Analysis: Graph Neural Networks and Legal Importance
- RAG Architecture: Combining Retrieval with Generation
- Lexis+ AI: Architecture and Capabilities
- Westlaw CoCounsel: Model Agnostic RAG Implementation
- vLex Vincent: Multi-Model Global Architecture
- Citation Verification Systems: Shepard’s and KeyCite
- Hallucination Rates and Accuracy Concerns
- Best Practices for Using AI Legal Research Tools
- Conclusion
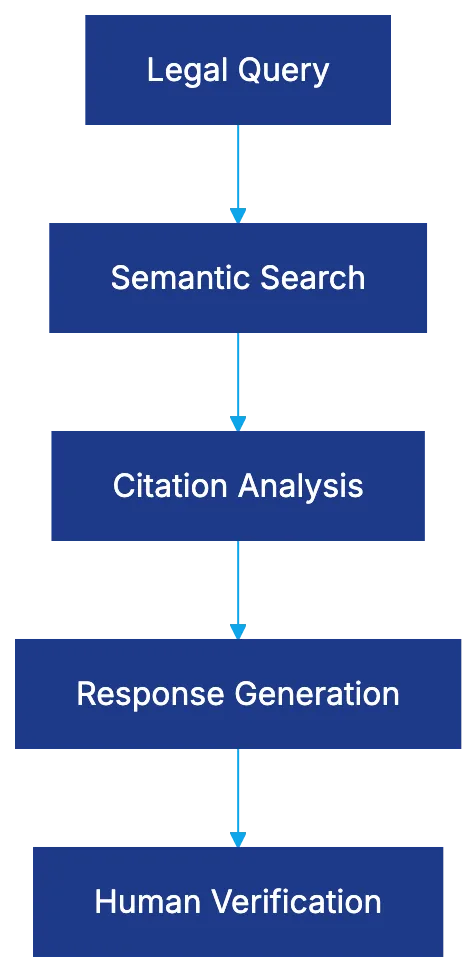
AI legal research tools](https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/ai-legal-research-tools-revolutionize-legal-industry-11612345678) are transforming the legal landscape. These tools facilitate faster case law discovery, smarter citation analysis, and quick answers to complex legal questions. Understanding the technology behind these tools is crucial for effective usage, as AI adoption in legal practice is accelerating rapidly. This guide delves into the architecture of tools like Lexis+ AI, Westlaw Precision with CoCounsel, and vLex Vincent AI, highlighting potential citation hallucinations and the technical foundations for responsible utilization.
Understanding Semantic Search vs. Keyword Search in Legal Research
AI Legal Research Technology Overview:

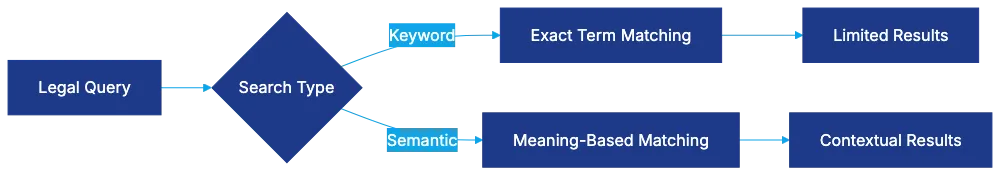
Legal research has traditionally depended on keyword matching, which has limitations, prompting the adoption of semantic search techniques. Semantic search offers an alternative by focusing on meaning rather than exact terms, converting legal documents into multi-dimensional embeddings to identify relevant cases. This AI process bridges gaps left by keyword searches, though results require legal citation verification.
Citation Network Analysis: Graph Neural Networks and Legal Importance
Semantic Search vs Keyword Search:
AI tools utilize graph analysis to map case law citations with Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). Nodes represent cases, and edges signify citations. This evaluates cases with significant precedential value using two approaches: up-the-tree traces citations backward and down-the-tree tracks subsequent treatments. Algorithms inspired by PageRank assess legal importance by identifying frequently cited cases.
RAG Architecture: Combining Retrieval with Generation
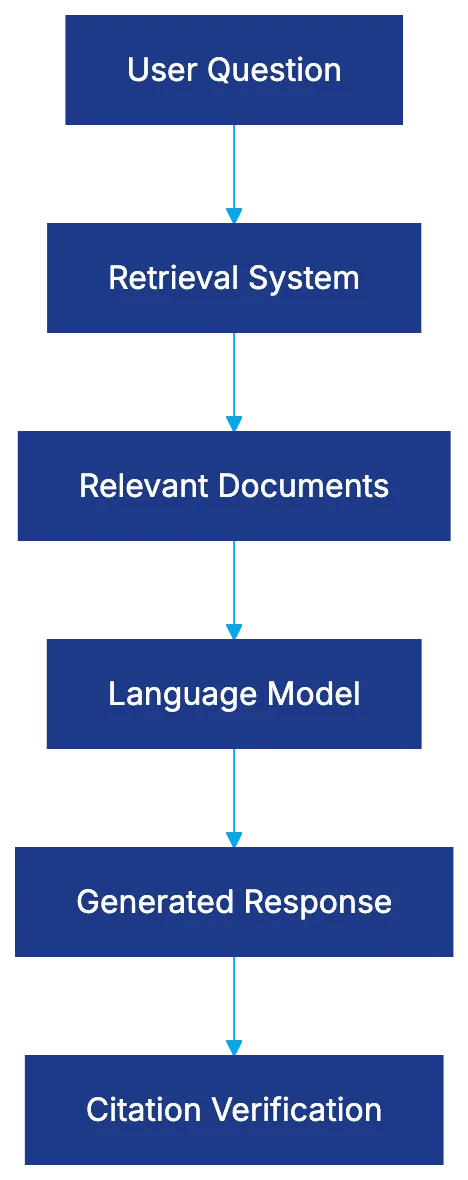
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture is integral to AI legal tools, separating retrieval from generation to minimize hallucinations. The retrieval system identifies relevant documents, feeding into a large language model to generate responses based on the retrieved content. The quality of retrieval is vital, though language models can still produce errors.
RAG Architecture in Legal AI:
Lexis+ AI: Architecture and Capabilities
Lexis+ AI employs a hybrid model using constrained databases and the Protégé AI Assistant for conversational research, integrating Shepard’s Citations to display case treatments by courts. It integrates Shepard’s Citations to display case treatments by courts. However, its closed-loop design limits accuracy, necessitating independent verification.
Westlaw CoCounsel: Model Agnostic RAG Implementation
Westlaw CoCounsel features a model-agnostic RAG architecture that grounds responses in retrieved content, with its Deep Research capability decomposing complex queries into multi-step plans. Its Deep Research capability decomposes complex queries into multi-step plans, resembling expert processes. KeyCite flags cases based on their treatment, but its hallucination rate surpasses that of Lexis+ AI, requiring thorough verification.
vLex Vincent: Multi-Model Global Architecture
vLex Vincent offers a global scope with a multi-model architecture across jurisdictions for comprehensive international research coverage, though document quality varies and lacks robust hallucination testing. Document quality varies and lacks robust hallucination testing, and the confidence threshold system aims to filter uncertain responses but demands verification.
Citation Verification Systems: Shepard’s and KeyCite
Shepard’s Citations and KeyCite are indispensable for verifying citation accuracy, utilizing signal and flag systems to indicate case treatment. Legal researchers must independently verify to avoid unfavorable precedents.
Hallucination Rates and Accuracy Concerns
Research from Stanford HAI highlights concerning hallucination rates in AI legal platforms, with Westlaw CoCounsel and Lexis+ AI demonstrating significant error rates, emphasizing the necessity for human verification of AI-generated research.
AI Legal Research Verification Workflow:
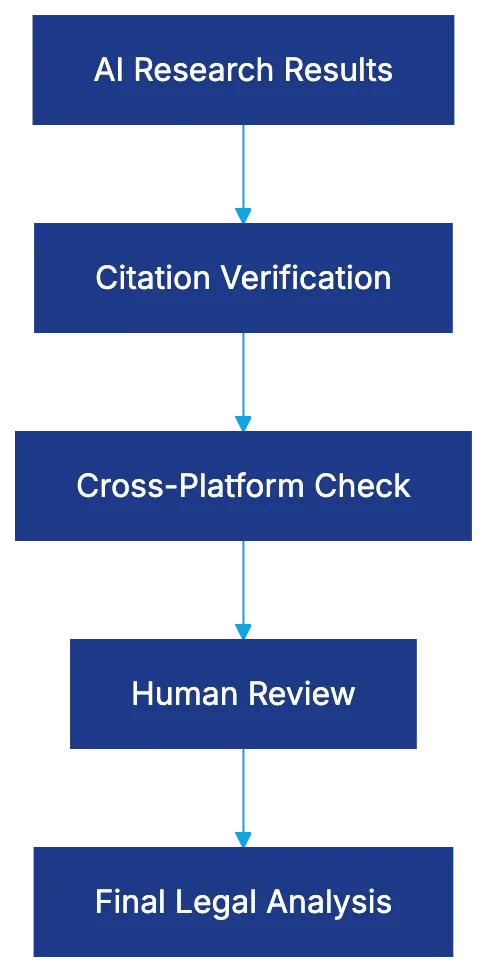
Best Practices for Using AI Legal Research Tools
- Use AI as a starting point: AI tools assist in identifying potential authorities and organizing complex questions, but results need thorough verification.
- Verify every citation: Ensure all cited cases align with your research using Shepard’s or KeyCite.
- Cross-check platforms: Utilize multiple AI tools to detect discrepancies needing further scrutiny.
- Thorough documentation: Maintain clear records of AI tool usage and research timelines.
- Complete training: Educate your team on AI tools’ capabilities and limitations.
- Policy development: Create policies for AI research standards and verification processes.
- Mix AI breadth with human depth: Use AI for quick surveys, but rely on human judgment for in-depth analysis.
Conclusion
AI legal research tools, while valuable, cannot replace human judgment and verification. Understanding the technology, maintaining rigorous verification practices, and establishing clear policies are essential for harnessing their full potential. Proper use enhances the speed and scope of AI case law research.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I start using AI legal research tools?
Begin by assessing the available AI tools like Lexis+ AI, Westlaw CoCounsel, and vLex Vincent. Most platforms offer trial versions or demos, allowing you to explore features and functionalities before committing. It's advisable to also participate in training sessions to understand the tools better.
What are the main differences between semantic search and keyword search?
Semantic search focuses on understanding the meaning behind words, allowing for more relevant results based on context and intent. In contrast, keyword search relies on exact word matching, which can lead to missed relevant cases. This shift improves the efficiency and accuracy of legal research.
What is the importance of citation verification?
Citation verification ensures that the cases you rely on are accurate and relevant to your research. Tools like Shepard's Citations and KeyCite indicate how cases have been treated in courts but require independent checks to avoid unfavorable outcomes. This step is crucial in maintaining the integrity of legal arguments.
What does the term 'hallucination' mean in the context of AI legal research?
In AI language models, 'hallucination' refers to instances where the AI generates incorrect or misleading information that does not align with factual sources. Research indicates that some legal AI tools exhibit significant hallucination rates, making it essential to verify AI-generated results against reliable legal texts.
How often should I cross-check results from different AI platforms?
It's advisable to cross-check results whenever there are significant discrepancies or if the stakes of the research are high, such as in litigation cases. Utilizing multiple platforms allows you to confirm findings and view a wider range of interpretations, which enhances the reliability of your legal research.
What best practices should I follow when using AI legal research tools?
Adopt a systematic approach: use AI for initial research, verify citations, cross-check results, and document your process. Training your team on limitations and capabilities of AI tools is also crucial. Establish clear policies for relying on AI research to maintain high standards and accountability.
Will AI legal tools replace traditional legal research methods?
AI legal tools are designed to complement traditional research, not replace it. While they improve efficiency and access to information, human judgment and expertise remain indispensable for thorough legal analysis and credible argumentation. Utilizing both methods effectively enhances overall research quality.
Related Articles

AI Contract Drafting Tools for Legal Professionals
Comprehensive guide to AI contract drafting tools, from conditional logic to platform comparisons. Learn how AI legal drafting differs from templates.
Conga: Revolutionizing Legal Technology for Professionals
Discover how Conga streamlines contract management and document generation for legal teams using Salesforce.
Malbek's Innovative Take on Contract Lifecycle Management
Explore how Malbek's conversational AI transforms contract lifecycle management for legal teams in mid-market and enterprise organizations.